
Analysis Service
ORANGE.I provides accurate test analysis and
consulting based on scientific and
objective data.
With over 30 years of experience in the industry
and technical
knowledge, our analysis experts
are here to support you.
Analyzing battery cell material properties, fine
sample components such as
foreign substances,
diverse organic and inorganic materials, and
performing
professional analysis on product
defects and failures
Battery Cell
& Raw Materials
By analyzing the components and structural properties of battery materials, parts, and cells helps better understand
battery performance and lifespan. ORANGE.I possesses core technologies that analyze lifetime characteristics,
changes in material conditions inside cells, and electrochemical properties.
-
4 Major Materials Analyzing
Analyzing the composition, shape, and structure of positive and negative electrode active materials, separators, and electrolytes to identify material type, mixing ratio, additive components, and component distribution; leveraging that information in material development; observing changes in state before and after deterioration; identifying the cause of deterioration; and applying it to improvement activities.
-
Non-destructive Analysis of Battery Cells
Visually analyzing the structure, defects, material distribution, and structural changes inside the battery through cutting-edge 3D CT technology based on X-ray transmission technology and indirectly verifying the internal state of the cell through electrochemical analysis.
-
Battery Parts Analysis
Examining the composition, structure, and surface treatment of materials used as parts, such as aluminum base, copper base, can, tab, pouch, etc., understanding their distributions, and defining the different physical attributes necessary for component materials.
By analyzing the components and structural properties of battery materials, parts, and cells helps better understand
battery performance and lifespan. ORANGE.I possesses core technologies that analyze lifetime characteristics,
changes in material conditions inside cells, and electrochemical properties.
Analysis Cases
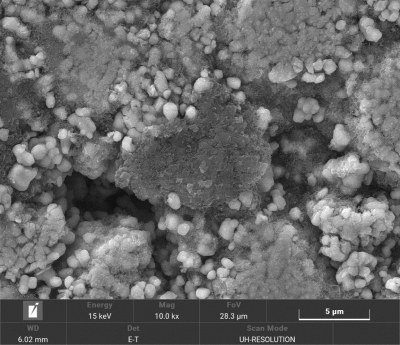
Cathode electrode
surface shape

Anode electode
surface shape

Separator surface
shape
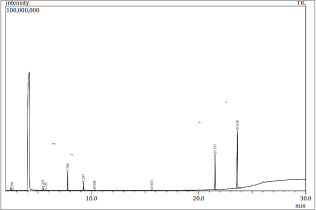
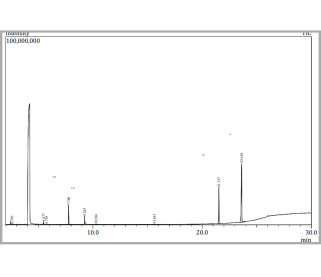
Main components of the
electrolyte in the cell
4 Major Materials Analysis Cases
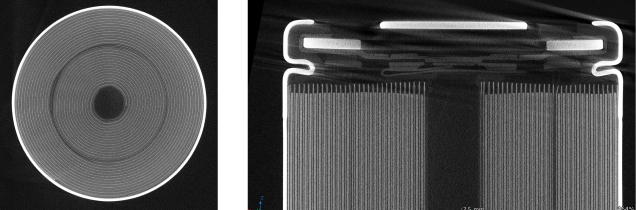
3D transmission shape of a cylindrical cell
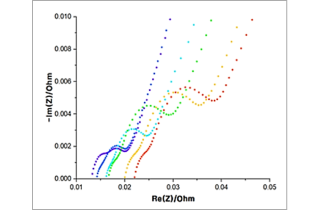
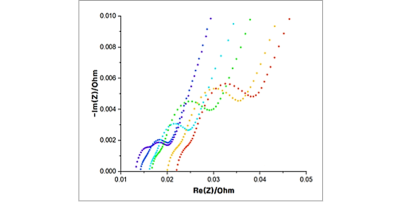
Impedance change according to life cycle
By analyzing the components and structural properties of battery materials, parts, and cells helps better understand
battery performance and lifespan. ORANGE.I possesses core technologies that analyze lifetime characteristics,
changes in material conditions inside cells, and electrochemical properties.
Analysis Cases
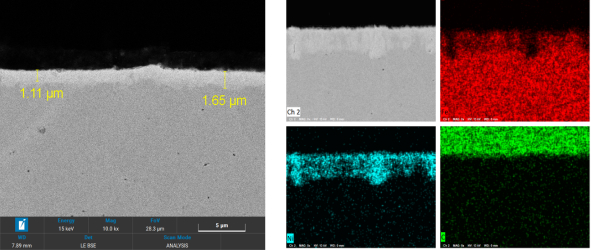
Ni plating layer distribution on the can surface
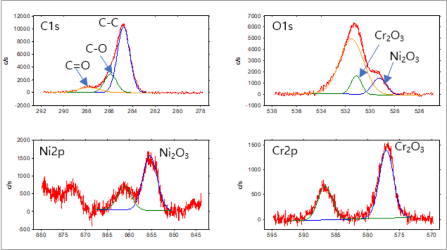
Bonding phase of the surface coating layer
Part material analysis example
ORANGE.I is equipped with precise sample pre-treatment technology and data interpretation technology to analyze the components of foreign substances
at the level of ㎛ to ㎜ and determine the source of inflow during processes or products such as batteries, semiconductors, food, and pharmaceuticals.
Analysis Items
Foreign substances injected during processes: checking the composition of extremely tiny foreign substances retained in the process.
Foreign substances on the product surface: assessing foreign substances remaining on the product surface and discovering the source of inflow using comparative assessment and comparison
Analysis Process
-
Sample
PretreatmentSeparating foreign substances and sampling
-
Organic Material Analysis
(micro-FTIR)Analyzing materials such as plastic, rubber,
fiber, and natural materials -
Inorganic Material Analysis
(FE-SEM/EDS)Analysis of materials such as
metal, glass, ceramics, Etc. -
Interpretation of
comprehensive resultsDetermining final results and
preparing the test report
ORANGE.I is equipped with precise sample pre-treatment technology and data interpretation technology to analyze the components of foreign substances
at the level of ㎛ to ㎜ and determine the source of inflow during processes or products such as batteries, semiconductors, food, and pharmaceuticals.
Analysis Cases
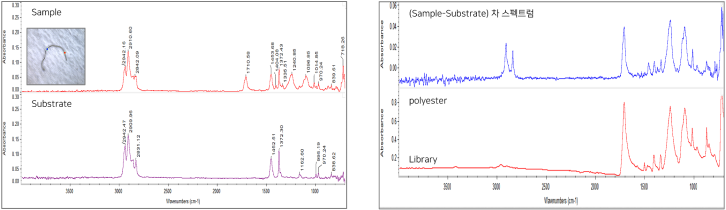
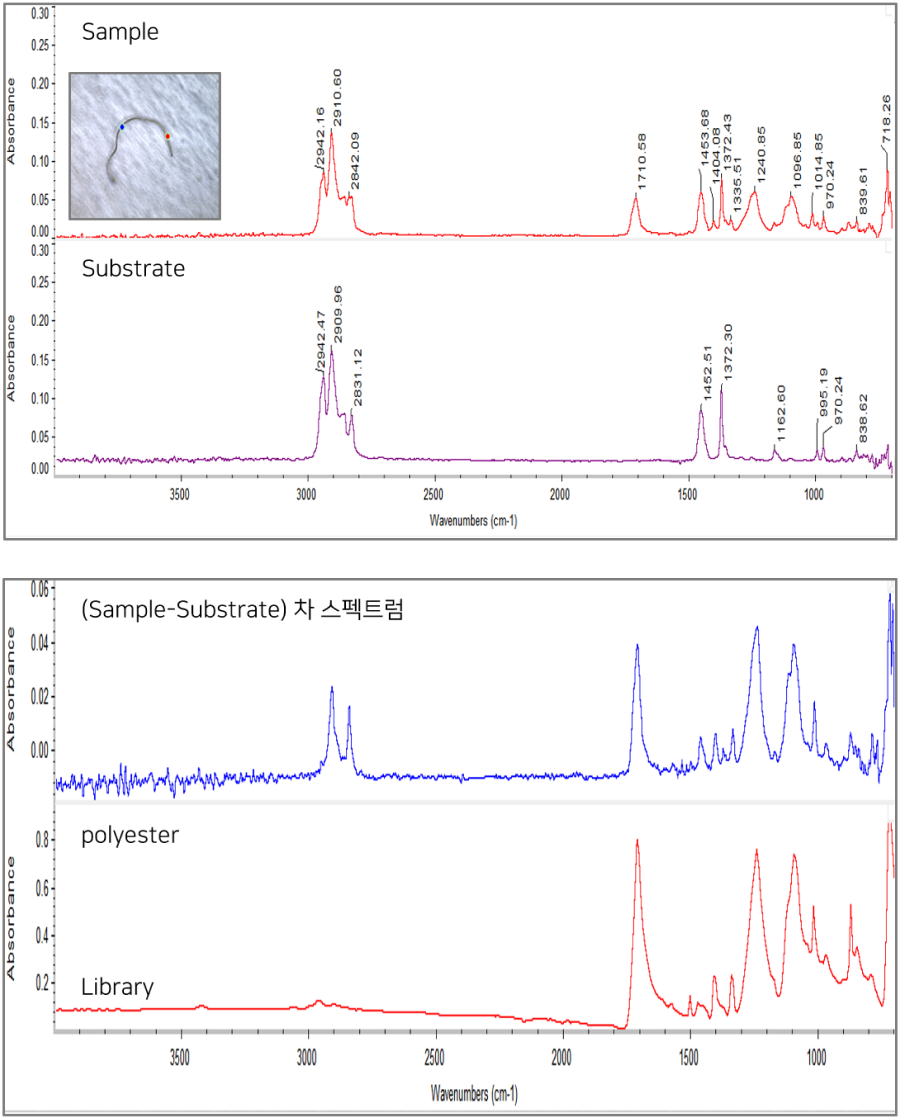
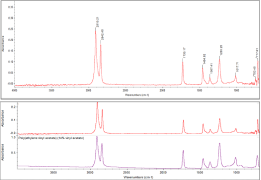
Analysis of foreign substances in the form of fibers of hundreds of ㎛ supplied from outside
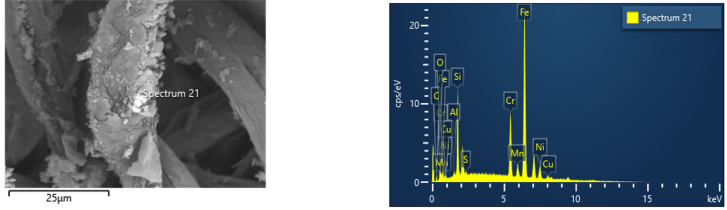

Analysis of foreign substances by collecting tens of ㎛ of foreign substances within the process
Organic & Inorganic
Materials
The composition, structure, and physical properties of organic and inorganic materials are essential factors in determining
product quality. ORANGE.I provides optimal analysis data by choosing an analysis approach that is suited for the customer's needs
and obtaining deep and broad data.
Organic & Inorganic
Material Analysis
| Item | Description | Example | Major Analytical Equipments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Organic | Chemical substances produced by living things that are generally classified as organic if they contain carbon compounds |
sugars, proteins, fats, hydrocarbons, plastics, rubber, fibers, natural substances, etc. |
FT-IR, Raman, GC-MS, NMR, XPS, Tof-SIMS, TGA, DSC |
| Inorganic | Any elements that are not organic | Minerals, metals, ceramics, glass, etc. | ICP-OES, ICP-MS, IC, XRF, XRD, XPS, SIMS, SEM-EDS, TEM |
The composition, structure, and physical properties of organic and inorganic materials are essential factors in determining
product quality. ORANGE.I provides optimal analysis data by choosing an analysis approach that is suited for the customer's needs
and obtaining deep and broad data.
Analysis Cases
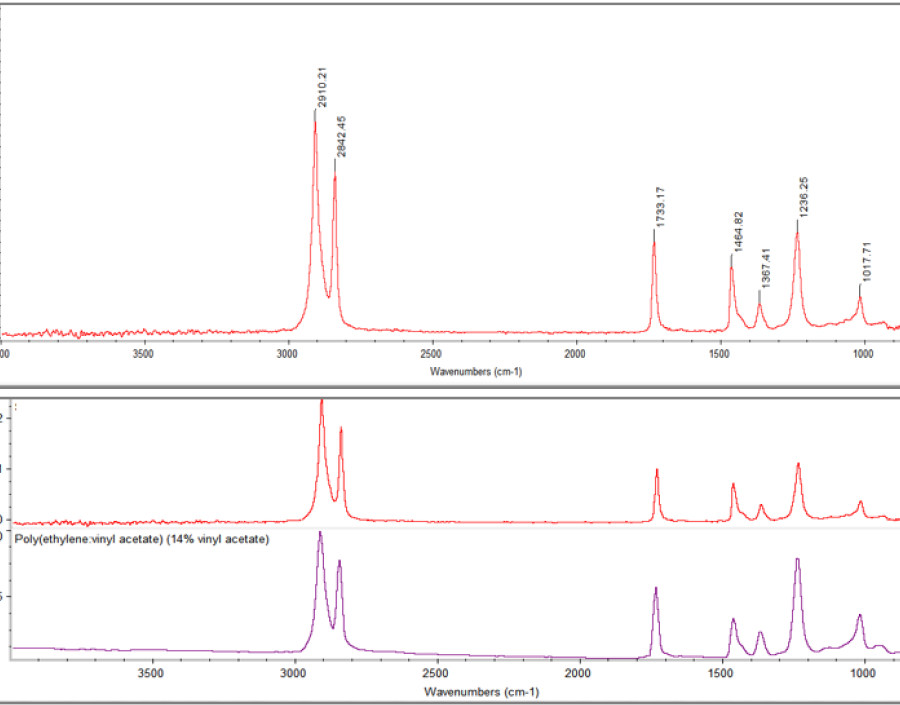
Investigating the organic materials
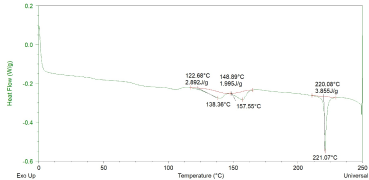
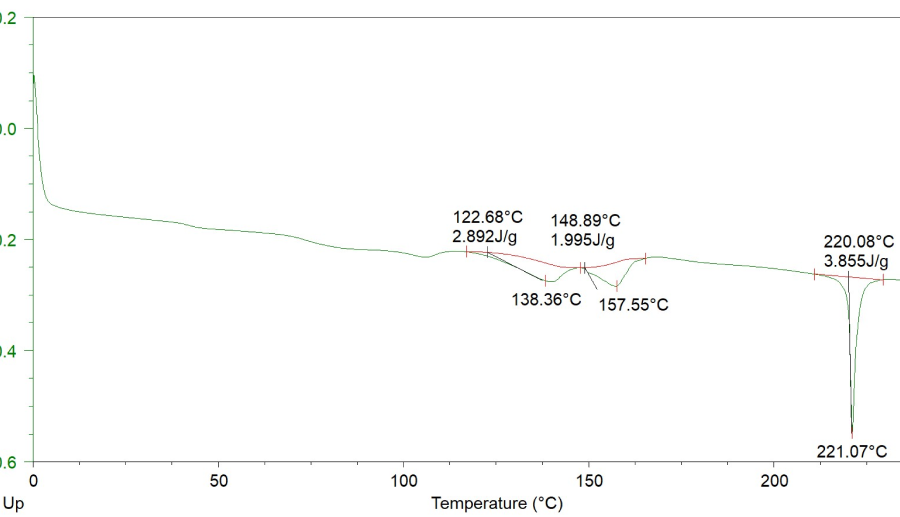
Verifying the thermal characteristics of the pouch
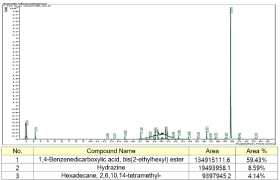
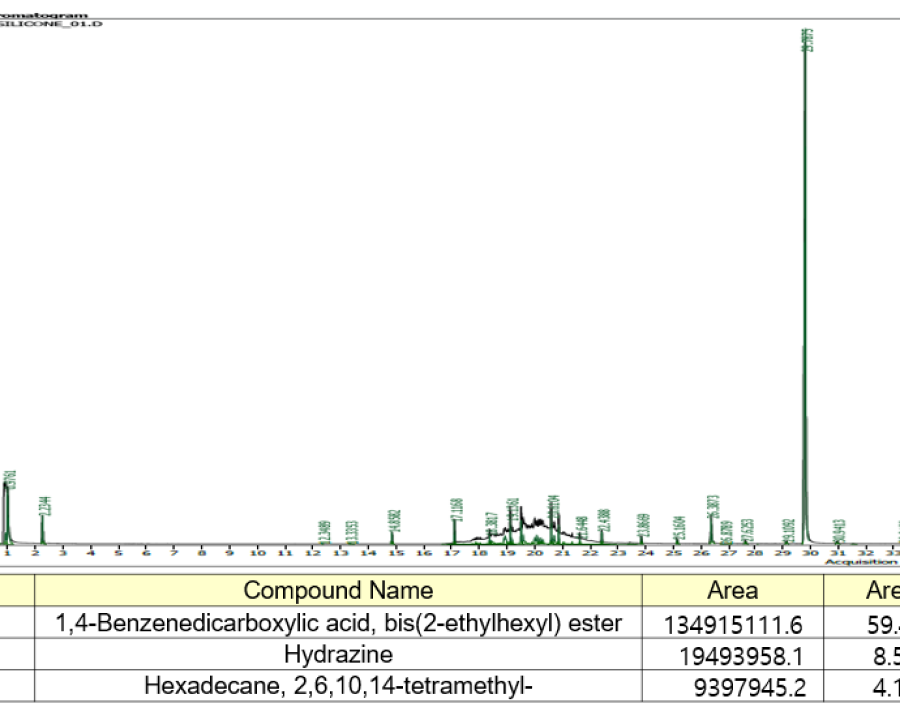
Detecting trace organic substances
remaining in the silicone
Analysis of organic materials

Observing the surface shape
of ceramic particles
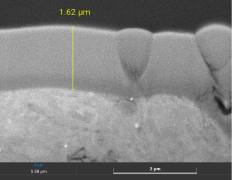
Watching the cross-section of the plating
layer formed on the metal surface
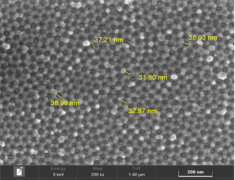
Checking the high-magnification
shape of the metal surface
Analysis of inorganic materials
Failure Analysis
ORANGE.I analyzes the causes of unexpected failures and defects that occur in products and parts as results of
environmental or physical stress. We deliver effective solutions to pressing challenges by maintaining frequent
communications with our consumers.
Failure Analysis
Process
-
Occurrence of
an issue -
Definition of
the problem- Defining defect phenomenon
- Discussing with customer
-
Establishment of
hypothetical scenario- Setting up a hypothesis
- Deciding the analysis method
-
Validation of
analysis and factors - Calculating analysis data
- Verifying significant
differences from hypothesis
-
Making
final conclusions- Producing final results
- Proposing improvement plans
Analysis Cases
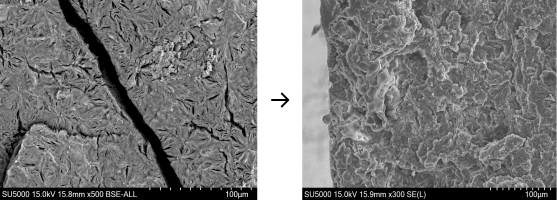
Analyzing the phenomenon of plastic breakage defects
and evaluating the material, hardness, etc. to determine the cause

Analyzing the corrosion caused by a defective pin hole
on a metal surface and identifying the cause
